Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com

Automatic External Defibrillators or AED's for short, are amazing devices that when applied to a sudden cardiac arrest patient, will sense the heart rhythm and if the person is in ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, will automatically deliver a shock to disrupt the unorganized rhythm and allow the heart to restart its proper rhythm. When used in the first minutes of a cardiac arrest, they can increase the chances of survival between 50 and 75%.

During a sudden cardiac arrest, the normal rhythm of the heart becomes erratic, with the cells of the heart "fibrillating," firing in all directions resulting in the muscles of the heart not being able to contract properly. Mechanically there is a loss of the pump to push blood to the heart and brain, electrically there is random firing that is not controlling the muscle to contract. Chest compressions will substitute for the mechanical contraction, forcing blood to the circulation of the heart and the brain, whereas the AED will interrupt the chaotic firing and allow the heart to restore a normal rhythm.
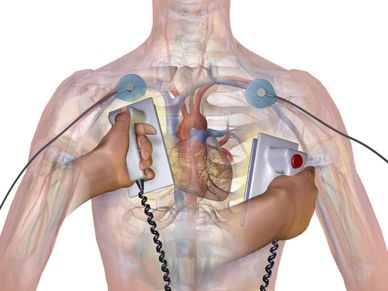
When the AED pads are applied to the right and left of the heart, the machine will sense the fibrillating rhythm and send an energy pulse through the heart. This pulse is strong enough to disrupt the disorganized firing of the cells and allow the natural pacemaker of the heart to resume controlling the heart. Most AED's will then instruct the bystander to begin CPR and provide audible assistance to help you provide the right rate and depth of compressions.
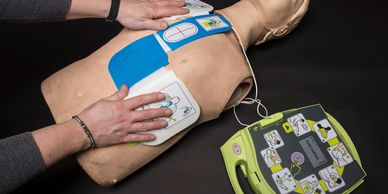
There are several different types of defibrillators. Doctors, nurses, and paramedics, carry manual defibrillators that have a wide availability of options for treating many heart dysrhythmias. Some first responders carry semi auto defibrillators, that require the bystander to push a shock button when prompted, and may display the rhythm on a screen on the AED.
Most public AED's are automatic.

No. Anyone responding as a bystander and attempting CPR and using an AED is protected by both the Good Samaritan Act, and the Chase McEachern Act.
The other thing to remember is that the AED will only deliver a shock to someone who's heart has stopped.
"You can't hurt, you can only help."
No. While training will help you function better in an emergency, to use an AED, take it out of its case, open the lid, press the on button and peel and stick the pads to the patients bare chest. All AED's have a diagram where to place the pads. Follow the AED's instructions and don't forget to call 911!
The Emergency Medical Dispatcher can help you through how to do CPR and use the AED.
If you want to take training, contact a local training provider
Providers approved to deliver emergency and standard first aid | WSIB
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.